Iran’s Tax System in 2025 Explained: A Guide for Foreign Businesses
Key Tax Insights for Foreign Investors in 2025

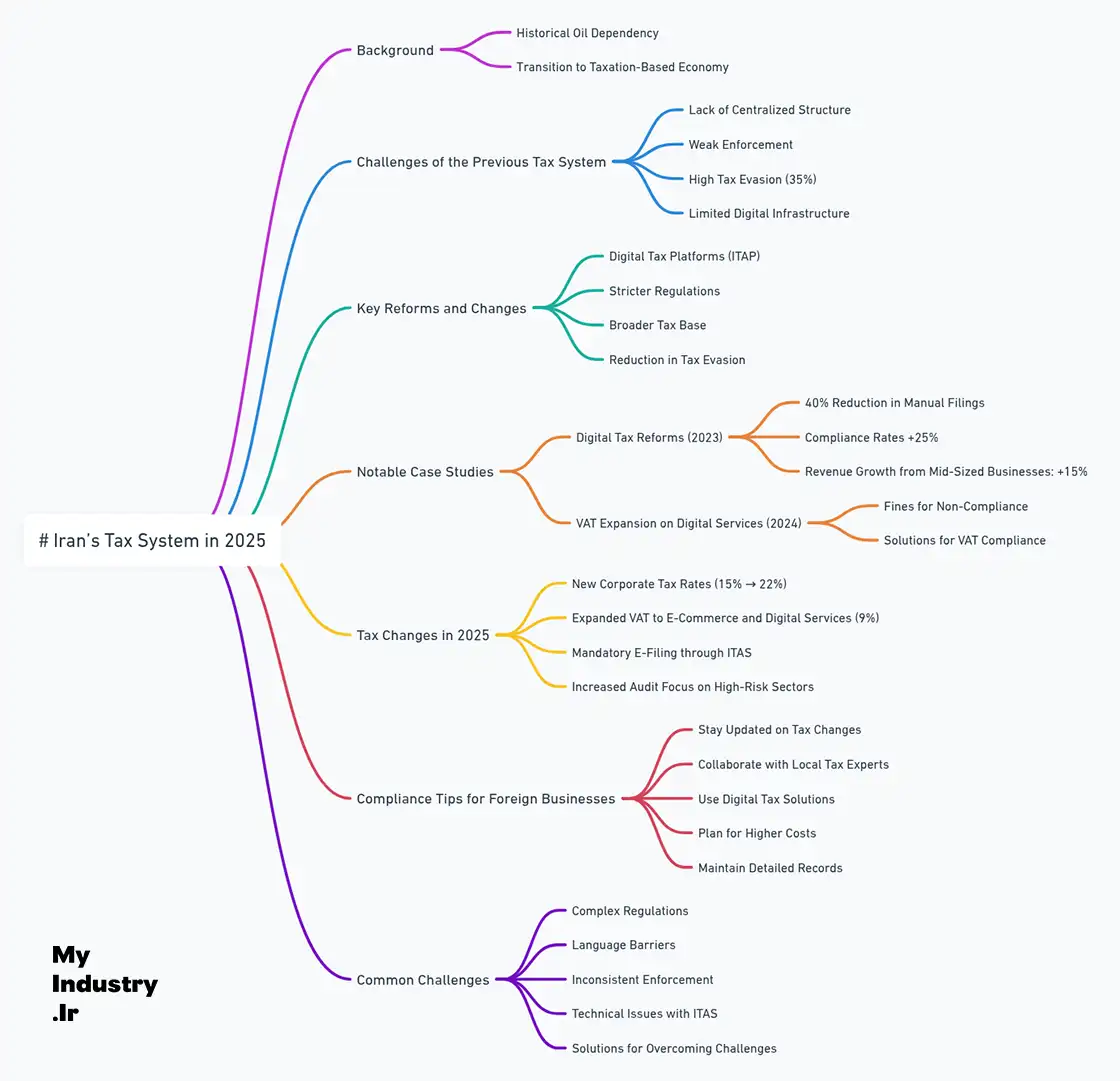
Iran’s Tax System in 2025 Explained
Iran’s Tax System in 2025 Explained plays a critical role for businesses aiming to enter the Iranian market. Historically, Iran’s economy was heavily dependent on oil, contributing to more than 50% of its national revenue until a decade ago. However, due to international sanctions and declining oil prices, the government had no choice but to seek alternative sources of income. This strategic shift marked a turning point, transforming taxation into a key pillar of the country’s financial model.
In the past, Iran’s tax system suffered from several challenges:
- Lack of a centralized tax structure
- Weak enforcement mechanisms
- High levels of tax evasion (estimated at 35% of potential tax revenue)
- Limited digital infrastructure for tax management
By 2025, significant reforms aim to address these issues. The government is introducing digital tax platforms, enforcing stricter regulations, and expanding the tax base. For foreign businesses, understanding these changes is essential to comply with the new rules and avoid penalties.
Case Study: Digital Tax Reforms in Action
In 2023, Iran launched an initiative to modernize its tax system through the Iran Tax Automation Program (ITAP). Within the first year:
- 40% reduction in manual tax filings
- Compliance rates improved by 25%
- Tax revenue from mid-sized businesses grew by 15%
For example, a mid-sized foreign logistics company in Iran reduced its tax filing errors by 30% after switching to the new system, avoiding penalties and optimizing its financial reporting.
From Oil Dependency to Taxation: A Strategic Shift
Iran’s economy is undergoing a transformation. For decades, oil exports made up over 80% of the country’s export revenue. However, external pressures—including falling global demand for fossil fuels—prompted the government to rethink its financial strategy. Iran’s Tax System in 2025 Explained this shift clearly: taxation is no longer just an administrative tool; it is now a core component of national policy.
Key elements of this transformation include:
- Increased Corporate Taxation: Tax rates in sectors like telecommunications, retail, and technology have increased from 15% to 22%.
- Broader Tax Base: Previously untaxed sectors, such as e-commerce and digital services, are now subject to taxation.
- Reduction of Tax Evasion: Strict audits and penalties have been implemented to reduce evasion, especially in high-risk sectors like import/export.
For foreign investors, adapting to this environment is critical. While taxation might seem more complex, these reforms offer greater predictability and transparency, making long-term planning easier.
Case Study: VAT Expansion Impact on E-Commerce
In 2024, Iran expanded VAT to cover digital services. A multinational software company faced a $50,000 fine for failing to register under the new rules. By adjusting its accounting processes and working with a local tax consultant, the company resolved the issue and optimized its VAT compliance for the following year.
Key Tax Changes in 2025
Here are the most important changes businesses should be aware of:
-
New Corporate Tax Rates:
Companies in key sectors like telecommunications and IT services will face tax increases, with rates rising from 15% to 22% in 2025. -
Expansion of VAT:
VAT now applies to digital services and e-commerce. Although the VAT rate remains at 9%, its broader application will impact many foreign companies. -
Mandatory E-Filing:
All businesses must file taxes through the Iran Tax Automation System (سامانه جامع مالیاتی ایران). Failure to comply will result in fines up to 20% of the tax owed. -
Stricter Audits:
The government has tripled its audit budget, focusing on high-risk industries. Import/export businesses are likely to be closely monitored.
Compliance Tips for Foreign Businesses
To succeed in Iran’s evolving tax environment, foreign businesses should:
- Stay Informed About Tax Changes:
Regularly check updates, especially in digital sectors. - Use Local Expertise:
Collaborate with a tax consultant familiar with Iranian laws. - Adopt Digital Solutions:
Utilize the Iran Tax Automation System to ensure compliance. - Plan for Increased Costs:
Adjust financial plans for rising tax rates. - Maintain Accurate Records:
Keep detailed documentation to avoid issues during audits.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Despite improvements, challenges remain. Here are the most common issues and how to address them: (If you are going to register a company in Iran, Read this)
-
Complex Regulations: Frequent changes can complicate compliance.
Solution: Work with local experts and stay updated through ITAS. -
Language Barriers: Tax documents are in Persian.
Solution: Hire bilingual accountants to ensure accuracy. -
Inconsistent Enforcement: Regional differences can cause uncertainty.
Solution: Build relationships with local authorities and document all transactions. -
Technical Issues in Digital Systems: Some businesses face delays with ITAS.
Solution: Train your finance team and establish internal review processes.

Final Words
Iran’s Tax System in 2025 Explained marks a turning point in the country’s economic strategy. With less reliance on oil and more focus on taxation, Iran is building a more sustainable financial model. While these changes bring challenges, they also create opportunities for businesses willing to adapt.
By staying informed, planning ahead, and using the right resources, foreign businesses can successfully navigate Iran’s evolving market and thrive.
A Comprehensive Overview of Iran’s Tax System in 2025: Key Changes, Reforms, and Practical Tips for Foreign Businesses. This mind map summarizes the main aspects of the evolving tax landscape in Iran.
Read more in Tax Automation System of Iran






